Avada, a popular WordPress theme installed on 600,000 websites, was prone to several vulnerabilities affecting version 6.2.2 and below that could allow a low-privileged user to edit, create or delete any page or post on the website.
Avada comes in three parts: a theme (slug: Avada) and two required plugins, Fusion Builder and Fusion Core (slugs: fusion-builder and fusion-core).
Content Injection & Stored XSS
In the “fusion-builder/inc/class-fusion-builder-library.php” script, Avada registers the fusion_builder_update_layout action to load the update_layout function via the AJAX API:
add_action( 'wp_ajax_fusion_builder_update_layout', [ $this, 'update_layout' ] );
...
...
/**
* Save custom layout.
*/
public function update_layout() {
check_ajax_referer( 'fusion_load_nonce', 'fusion_load_nonce' );
if ( isset( $_POST['fusion_layout_id'] ) && '' !== $_POST['fusion_layout_id'] && apply_filters( 'fusion_global_save', true, 'ajax' ) ) {
$layout_id = wp_unslash( $_POST['fusion_layout_id'] ); // phpcs:ignore WordPress.Security.ValidatedSanitizedInput
$content = isset( $_POST['fusion_layout_content'] ) ? wp_unslash( $_POST['fusion_layout_content'] ) : ''; // phpcs:ignore WordPress.Security.ValidatedSanitizedInput
$to_replace = addslashes( ' fusion_global="' . $layout_id . '"' );
$content = str_replace( $to_replace, '', $content );
// Filter nested globals.
$content = apply_filters( 'content_save_pre', $content, $content, $layout_id );
$post = [
'ID' => $layout_id,
'post_content' => $content,
];
wp_update_post( $post );
}
wp_die();
}
The function is used to update the content of the fusion_element or fusion_template post type whose ID is fusion_layout_id. It doesn’t verify if the user is allowed to edit the corresponding post ID nor if the post type is the expected one. The function only checks the fusion_load_nonce security nonce, which is populated by the admin_scripts function in the “fusion-builder/inc/class-fusion-builder.php” script:
add_action( 'admin_enqueue_scripts', [ $this, 'admin_scripts' ] );
...
...
public function admin_scripts( $hook ) {
...
...
if ( ( 'post.php' === $pagenow || 'post-new.php' === $pagenow ) && post_type_supports( $typenow, 'editor' ) ) {
...
...
// Localize Script.
wp_localize_script(
'fusion_builder',
'fusionBuilderConfig',
[
'ajaxurl' => admin_url( 'admin-ajax.php' ),
'fusion_load_nonce' => wp_create_nonce( 'fusion_load_nonce' ),
...
...
]
);
...
...
The nonce is echoed in the source of the HTML page when a logged-in user accesses “post-new.php” to edit or create a new post:
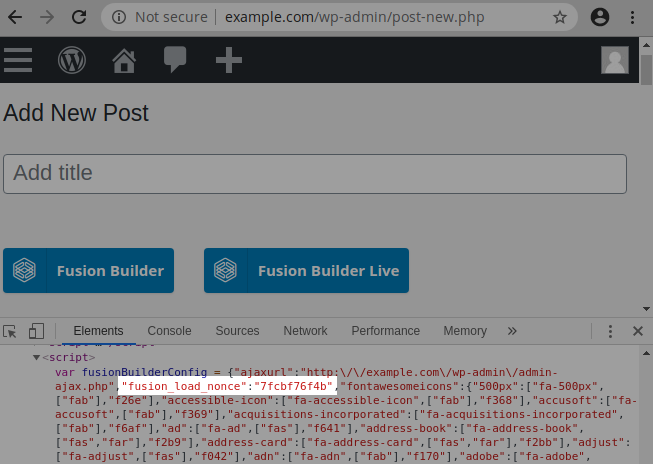
A low-privileged user such as a contributor can copy the nonce and modify any existing page or post on the website. It is also possible to inject JavaScript code by using the [fusion_code] attribute, which is enabled by default:
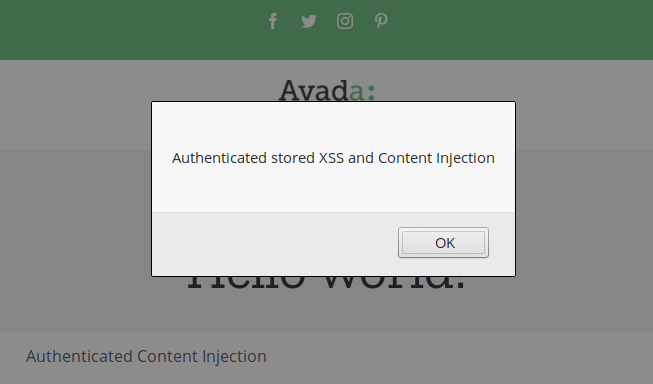
Arbitrary Post Deletion
Avada registers the fusion_builder_delete_layout action in order to load the delete_layout function:
add_action( 'wp_ajax_fusion_builder_delete_layout', [ $this, 'delete_layout' ] );
...
...
/**
* Delete custom template or element.
*/
public function delete_layout() {
check_ajax_referer( 'fusion_load_nonce', 'fusion_load_nonce' );
if ( isset( $_POST['fusion_layout_id'] ) && '' !== $_POST['fusion_layout_id'] ) {
$layout_id = (int) $_POST['fusion_layout_id'];
if ( '' === $layout_id ) {
die( -1 );
}
wp_delete_post( $layout_id, true );
}
wp_die();
}
Here too, the user capability and the post type aren’t checked, the function relying only on the same security nonce. A logged-in contributor can delete any post or page on the website.
Arbitrary Post Creation
The fusion_builder_save_layout AJAX action used to call the save_layout function is prone to the same type of vulnerability: A logged-in contributor can create a post, select several parameters (post type, post status, slug etc), as well as inject JavaScript code with the [fusion_code] attribute.
Recommendations
Update immediately if you have version 6.2.2 or below installed.
If you are using our web application firewall for WordPress, NinjaFirewall WP Edition (free) and NinjaFirewall WP+ Edition (premium), you are protected against this vulnerability since April 23, 2020.
Timeline
The vulnerability was reported to the authors on April 23, 2020 and a new version 6.2.3 was released on April 24, 2020.
Stay informed about the latest vulnerabilities
- Running WordPress? You can get email notifications about vulnerabilities in the plugins or themes installed on your blog.
- On Twitter: @nintechnet
